Each available host type within the software comes pre-configured within an XML file in the \hosts\preconfigured directory. If a pre-configured host is activated, its XML file is copied to the \hosts directory and is then updated as the user further configures the host through the panels.
A host XML file is generally formatted as follows:
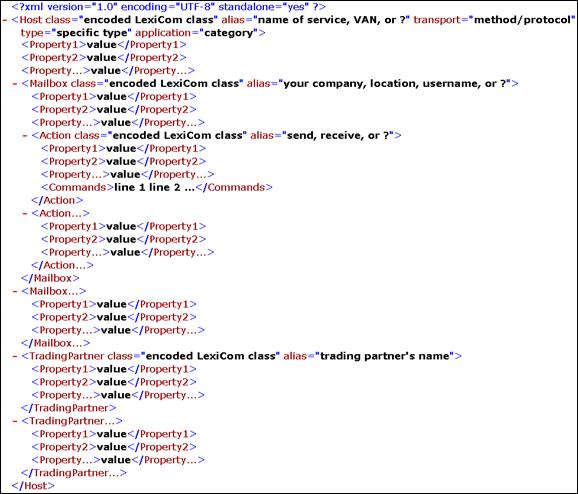
- One and only one <Host> element exists in the file.
- <Host> may contain zero or more <Mailbox> elements and zero or more <TradingPartner> elementss.
- <Mailbox> may contain zero or more <Action> elements.
- The class="path" identifies the VersaLex module that corresponds to this host type and tree level. It is a java class path relative to the base VersaLex bean package.
- The alias="value" cannot contain the backslash character (\).
- <Property1>, <Property2>, <Property...> do not actually exist. Some common property names and possible values do exist, but most are dependent on the specific host type.
- <Address>
- The server address, either a fully-qualified name (recommended) or an IP address.
- <Port>
- The server port, either a specific port number or -1 to indicate the default port for the protocol.
- <Connecttype>
- The connection type. Possible values are:
- 0: system default
- 1: direct internet access
- 2: LexRas dial-up connection
- 3: GXS IBC dial-up connection
- <Phonebookentry>
- Existing Windows RAS phonebook entry
- <Ibcusername>
- GXS IBC account username
- <Ibcpassword>
- GXS IBC account password
- <Inbox>
- Any local or shared directory
- <Outbox>
- Any local or shared directory
- <Sentbox>
- Any local or shared directory
- <Notes>
- Any pertinent information
- <Notes>
- Any pertinent information
- <Commands>
- Formatted command lines and syntax specific to hosts
- <Messages>
- Messages logged the last time the action was run
- <Notes>
- Any pertinent information
All pre-configured hosts are not created equally. The more generic host types contain little or no properties, while the more specific host types may contain almost all the required properties. The more information contained in the pre-configured host file, the less information the user must provide when the host is activated.
For example, the following generic HTTP/s host file provides no property values.

If you want to start with the generic HTTP/s host to connect to our example ABC VAN host, use the Cleo Harmony configuration panels to provide values for the following properties.

The best way to learn a property name and possible values for a specific host type is to use the Cleo Harmony UI to configure the host and then interrogate the XML file.