The following describes how to configure certificate manager options, including how you want to work with certificate revocation lists (CRLs) and trusted service lists (TSLs)..
- In the web UI, go to Administration > Certificate Management > Options. In the native UI, open the Certificate Manager Options dialog box – go to Tools > Certificate Manager or click the Certificates button in the tool bar and then select Configure > Options.
-
Select options from the Acceptance Criteria section.
- Check certificate validity period – display certificates that are expired or within the warning period (15 days) in red and orange, respectively.
- Check certificate issuer’s CA signature – verify the issuer’s signature when building the certificate chain.
- Check certificate verification – check the validity of
the certificate’s signature algorithm and that it can be used within the current
environment. When in FIPS mode, this setting is on by default and cannot be
disabled. When not in FIPS mode, this setting defaults to off. If a certificate
fails the verification check, it is marked with
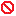 .
.
-
In the Revoked Certificates section, select Check
Revoked Certificates to check the revoked status for each user and CA
certificate and specify a value in the every [n] hours to
control how often the check occurs. by using either the certificate’s OCSP (Online
Certificate Status Protocol) URL or CRL (Certificate Revocation List) URL. If a
revoked certificate is found, it is marked with
 and cannot be used during file transfers, whether as a
server or client certificate, for signing or encryption, and so on. If it is a CA
certificate, its issued certificates also cannot be used. In addition to checking
CRLs actually contained within the certificates in the store, you can specify
additional CRL URLs provided by certificate authorities can
be configured and checked, if necessary.
and cannot be used during file transfers, whether as a
server or client certificate, for signing or encryption, and so on. If it is a CA
certificate, its issued certificates also cannot be used. In addition to checking
CRLs actually contained within the certificates in the store, you can specify
additional CRL URLs provided by certificate authorities can
be configured and checked, if necessary.
-
Optional. Click View Last Results… to see the status of the
certificate revocation checks.
Each OCSP and CRL URL is listed along with the status result. Possible results are:
- No revoked certificates found
- Revoked certificate(s) found
- Check error: …
- In the Trusted Service List seciton, select the Import Trusted Service (Status) List check box to download and import the configured TSL URLs every [n] hours. A TSL contains a set of CA certificates to be automatically trusted. Whether a CA certificate is added or removed from the TSL, it is likewise added or removed from the local certificate store. Click Import Now to start a new import in the background.
- In the Logging section, select the Enabled check box and then select a log level. A High log level is recommended while debugging a problem. You can find the debug log file can be found under the home directory at logs\CertMgrLogfile.txt. It contains information relative to security providers, certificate parsing, chaining, and usage, and UI invocation. Because the debug file will continue to grow, you should only enable certificate debug logging while you are investigating an issue, and you should disable it once the investigation is complete.
-
Click View Last Results… to see the status of the
certificate revocation checks.
Each OCSP and CRL URL is listed along with the status result. Possible results are:
- No revoked certificates found
- Revoked certificate(s) found
- Check error: …
- Click Save (web UI) or OK (native UI).